Stainless Steel 304
Introduction to Stainless Steel 304
Stainless steel 304 is a type of stainless steel with main components including iron, chromium, nickel, etc. It is one of the most common stainless steel types used in various industries and fields such as automotive, shipbuilding, construction, household appliances, etc.
The properties of Stainless Steel 304 include high durability, corrosion resistance, and oxidation resistance. This material has advantages in terms of rust resistance, easy surface cleaning, and health safety.

Composition of Stainless Steel 304
Stainless Steel 304 (also known as 304 stainless steel) is an alloy that consists of various elements. The main components of Stainless Steel 304 are as follows:
- Iron (Fe): From 66.345% to 74%, the main component of the material.
- Chromium (Cr): Approximately 18%. Chromium provides corrosion resistance and forms a surface oxide layer, enabling the material to withstand corrosive environments and chemical exposure.
- Nickel (Ni): Approximately 8%. Nickel provides corrosion resistance and enhances durability.
- Carbon (C): Typically below 0.08%. The low carbon content helps Stainless Steel 304 avoid brittleness and provides its ductility and ease of processing.
- Manganese (Mn): Approximately 2%. Manganese improves mechanical properties and hardness.
- Silicon (Si): Approximately 1%. Silicon enhances oxidation resistance and improves welding properties.
- Phosphorus (P), sulfur (S), copper (Cu), and other trace elements may also be present in Stainless Steel 304, but in very small amounts.
Properties of Stainless Steel 304
Physical Properties
Stainless Steel 304 has the following basic physical properties:
- Hardness: Ranging from 70 HB to 92 HB, depending on the processing and heat treatment. It is relatively ductile and can be bent.
- Color: Bright silver
- Density: Approximately 8 g/cm³, relatively high compared to many other materials. This means it has a large mass per unit volume.
- Melting Temperature: Around 1400-1450°C (2552-2642°F), depending on the composition and manufacturing method.
- Thermal Expansion Coefficient: Approximately 17-18 x 10^(-6) °C^(-1) in the temperature range of 20 – 100°C (68-212°F).
- Electrical Conductivity: Poor electrical conductivity, with an electrical resistivity ranging from 70 to 80 microohm·cm. To put it in perspective, the electrical resistivity of wood under normal conditions is approximately 10^9 to 10^14 ohm·m.
- Thermal Conductivity: Around 16.3 W/m·K at 100°C (212°F). This means it has relatively good thermal conductivity.
Chemical Properties
Stainless Steel 304 has the following basic chemical properties:
- Corrosion Resistance: Good corrosion resistance in water, air, and many weak and neutral acid solutions. The presence of chromium in the material forms a protective oxide layer on the surface, protecting the steel from corrosion.
- Oxidation Resistance: Good oxidation resistance, not easily oxidized under the influence of air and high temperatures.
- Acid Resistance: Resistance to weak and neutral acids such as acetic acid, lactic acid, and citric acid. However, it may be affected by strong acids such as nitric acid and sulfuric acid at high concentrations.
Classification of Stainless Steel 304
Stainless Steel 304 is commonly classified based on the carbon content in the material, as the carbon content directly affects the properties of this type of material.
Stainless Steel 304
This is the standard version of Stainless Steel 304 and the most common type. It primarily consists of chromium (18-20%), nickel (8-10.5%), iron (66.345% to 74%), along with other elements such as manganese, silicon, carbon, and trace elements. It has good corrosion resistance and oxidation resistance, meeting various general requirements in industrial and commercial applications.
Stainless Steel 304L
Stainless Steel 304L is a version with a lower carbon content compared to Stainless Steel 304, where “L” stands for Low. The carbon content in Stainless Steel 304L is limited to below 0.03%, reducing the formation of carbides during welding. This provides better corrosion resistance in acidic environments. However, the material will have lower hardness.
Stainless Steel 304H
Stainless Steel 304H is a version with a higher carbon content compared to Stainless Steel 304, where “H” stands for High. The carbon content in Stainless Steel 304H ranges from 0.04% to 0.10%. This increased carbon content creates a stronger crystal structure, improving hardness and heat resistance of the material. Stainless Steel 304H is often used in applications that require higher strength and heat resistance.
Note that Stainless Steel 304, Stainless Steel 304L, and Stainless Steel 304H have similar chromium and nickel compositions but differ in carbon content. The choice between these versions depends on the specific requirements and conditions of the application.
2 / 2
Applications of Stainless Steel 304
Known as the most widely used stainless steel, Stainless Steel 304 is utilized as a material for manufacturing machinery and everyday objects. Its popularity stems from its characteristics, including durability, good chemical resistance, and high hardness.
Some examples of the application versatility of Stainless Steel 304 include:
- Chemical industry: For chemicals with mild corrosive properties, Stainless Steel 304 can directly handle them. Therefore, this material is suitable for making tanks, pipes, various pipe fittings, valves, and more.
- Household items: Stainless Steel 304 is suitable for manufacturing various household appliances, especially kitchenware (pots, pans, spoons, knives, etc.) and bathroom fixtures (faucets, showerheads, sinks, etc.).
- Construction: With its excellent load-bearing capacity, bright surface, and resistance to oxidation, this material is used for structural reinforcement and crafting decorative interior items under normal working conditions.
These are just a few common applications of Stainless Steel 304, but it is also used in various other industries such as automotive, aerospace, renewable energy, water treatment, machinery manufacturing, and many more. The diversity and versatility of Stainless Steel 304 make it a popular and preferred material in numerous fields.

Some Considerations When Using Stainless Steel 304
Stainless Steel 304 is widely used as the primary material for many different devices and objects. Based on the characteristics of this material, it is important to take note of the following considerations to ensure that the equipment and objects are not damaged or affect the durability of the products.
During usage and the design and fabrication process, the following issues should be considered when using Stainless Steel 304:
- Operating fluid: This material can be used for various types of fluids, including water, gas, and some mildly corrosive chemicals. They have no adverse effect on the material’s durability. However, for highly corrosive substances or high-concentration saltwater, direct contact with Stainless Steel 304 should be avoided.
- Temperature and structure: When using Stainless Steel 304 to fabricate devices that operate under harsh conditions (high temperature and high impact force), factors such as thermal expansion and material hardness should be taken into account. Based on these parameters, the structure should be appropriately designed to suit the working conditions.
- Welding process: During the welding process of Stainless Steel 304, attention should be paid to avoid creating a heat-affected zone by controlling the temperature and welding time. The use of suitable welding materials and precise welding techniques is necessary to ensure the corrosion resistance and mechanical properties of the structure.
How to Identify Stainless Steel 304
In many cases, it is necessary to distinguish Stainless Steel 304 from other materials. Common situations include selecting materials from a stock with various options or purchasing materials in the market. Since Stainless Steel 304 has a similar appearance to many other stainless steel grades, it can be challenging to differentiate. To address this issue, the following methods can be applied:
- Check for markings or codes: Stainless Steel 304 is often marked with symbols or codes such as “304,” “18/8,” or “A2.”
- Magnetic test: Stainless Steel 304 is a non-magnetic steel. Use a magnet to test the product. If the magnet does not strongly attract or there is no significant magnetic effect, it could be Stainless Steel 304.
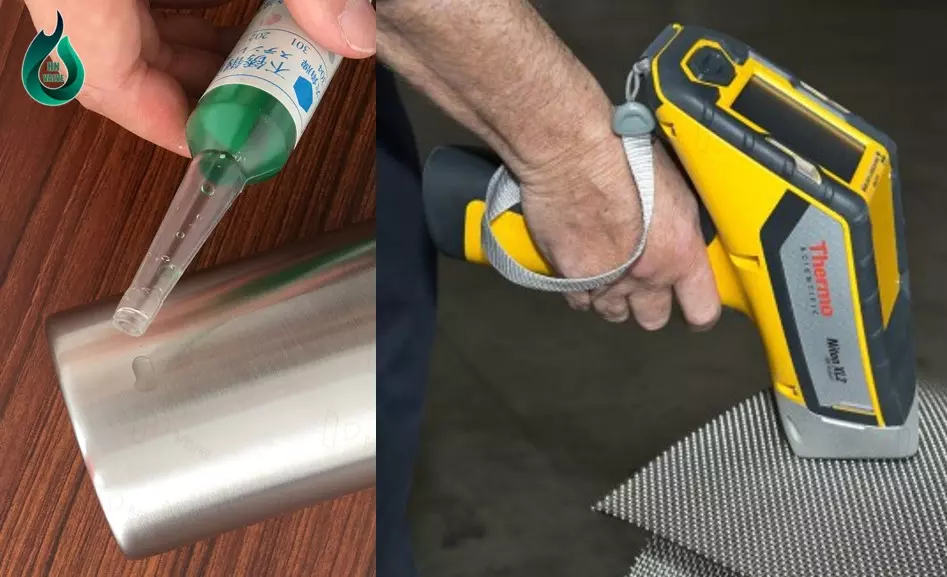
- Nitric acid test: You can use nitric acid to test the corrosion resistance of Stainless Steel 304. Exercise caution when performing this method and ensure compliance with safety regulations. If the product is not corroded or shows only a mild reaction, it could be Stainless Steel 304.
- Utilize analytical equipment: Analytical equipment can determine the main components of a material, helping to identify whether it is Stainless Steel 304 or not. However, this method requires the use of specialized equipment and should be performed by experts.
Note that testing Stainless Steel 304 may require knowledge and experience. If uncertain, consult experts or reputable suppliers to accurately determine the material type.

See more about PVC plastic.