Oil flow meter
Giá gốc là: 1.000.000 ₫.900.000 ₫Giá hiện tại là: 900.000 ₫.
Cập nhật lần cuối ngày 13/08/2025 lúc 10:30 sáng
The flow meter for measuring oil flow plays an important role in various systems, machinery, and vehicles. These products come in a diverse range, and they perform well in measuring the flow rate of various types of oil as well as high-viscosity fluids.
In this article, we will explore more useful information related to oil flow meters.
What is an oil flow meter?
An oil flow meter is a type of flow meter specifically designed to measure the flow rate of gasoline, oil, diesel, and other high-viscosity fluids.
These devices measure flow rates by directly installing them on pipelines where oil or the measured fluid passes through. Thanks to the specially designed flow sensing component placed inside the meter (such as turbine blades, gear pair, or any other type of sensor), these components interact with the flow of oil as it passes through the meter, creating rotational motion. This motion is then transmitted and transformed through a system to drive a mechanism or counter, ultimately displaying the value on the meter face.
There are many types of oil flow meters, but we can categorize them into two main types:
- Mechanical oil flow meters: The notable feature of mechanical oil flow meters is that they do not require power to operate.
- Electronic oil flow meters: The prominent advantages of electronic oil flow meters are their high accuracy in measuring flow rates and their ability to easily collect flow data.

The importance of measuring oil flow
In practical working conditions, measuring the flow rate of various types of oil plays a crucial role. Here, measuring oil flow is a general term for the task of measuring the flow rate of fluids, including gasoline, diesel, lubricating oils, and more.
For gasoline and diesel, which are high-value fluids, measuring their flow rate is essential and, in many cases, mandatory. It helps determine the unit price of these products during the buying and selling process. In production and transportation, the amount of fuel used for machinery and vehicles needs to be accurately calculated and balanced to enhance competitiveness with other products.
Lubricating oils, coolant oils, and other types of oils are often applied in machinery to serve the production and manufacturing processes. Besides their high cost, in many cases, the quantity of oil required for machines must be accurately supplied to ensure precise operations.

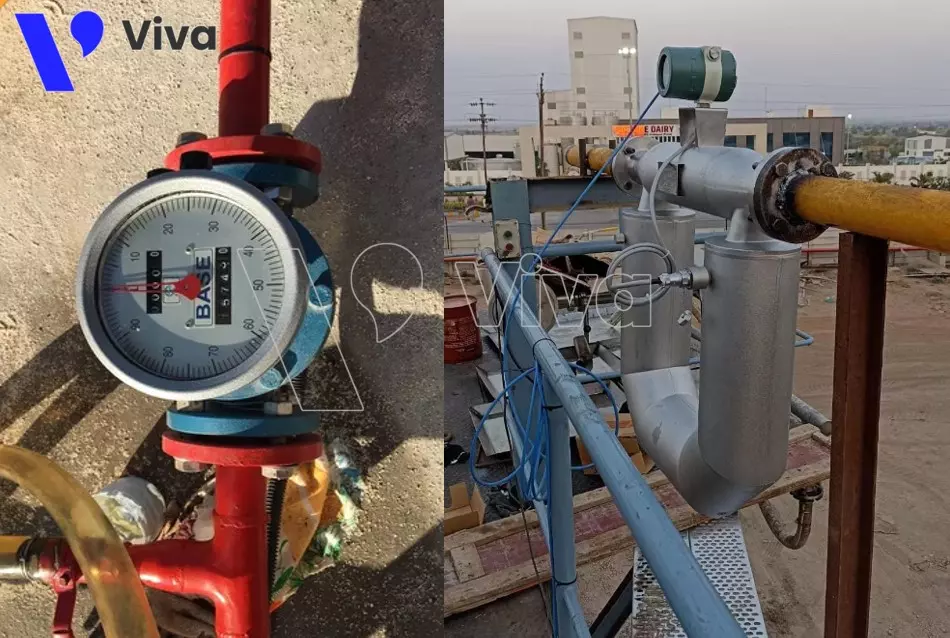
Two basic installation types of oil flow meters
To measure oil flow, our devices are mostly installed on pipelines, allowing the measured fluid to flow through the meter’s body. To achieve this, the meter body must be designed with appropriate installation types that align with the pipeline. Let’s explore these installation types together.
Threaded oil flow meters
Flow meters for measuring oil flow that use threaded installation types are commonly known for their compact design. Inside the body of these meters, they use turbine blade components or a pair of oval-shaped gears to interact with the flow velocity of the fluid.
The meter body is usually designed to be relatively small in size, with threaded connections on both sides of the meter body. Manufacturers provide us with options for internal or external threads. The thread size is designed according to standards to ensure easy installation.

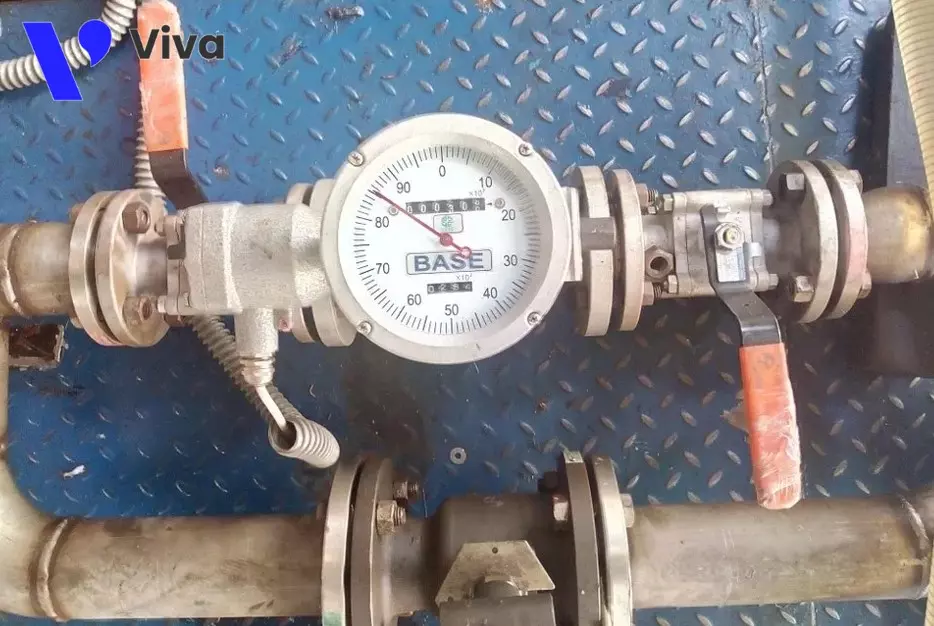
Flanged oil flow meters
Flanged oil flow meters are designed with flanged connections on both ends of the meter body. The common characteristic of these devices is their large size. They can be either mechanical or electronic meters. While threaded installation types offer convenience and quick installation, flanged installation types excel in their ability to withstand high impact forces and provide high stability. Moreover, with larger-sized devices, flanged installation is easier.

Classification of oil flow meters
There are various types of oil flow meters, each with its own operating principles and unique structures. Some types are variations of basic flow meters. Let’s explore some commonly used types of oil flow meters.
Turbine-type oil flow meters
The turbine-type flow meters use a turbine blade component placed inside the valve body. When oil flows through, it causes the turbine blades to rotate. The rotational speed of the turbine blades is proportional to the flow velocity of the oil passing through the meter body. This rotational speed is then sensed and encoded into an electrical signal by a special component.
The signal is then transmitted through a signal processing unit to calculate the appropriate flow rate value.
This product line has many variations, featuring compact sizes and operation powered by lithium batteries. They provide the ability to measure the flow rate of oil, gasoline, and various other fluids.

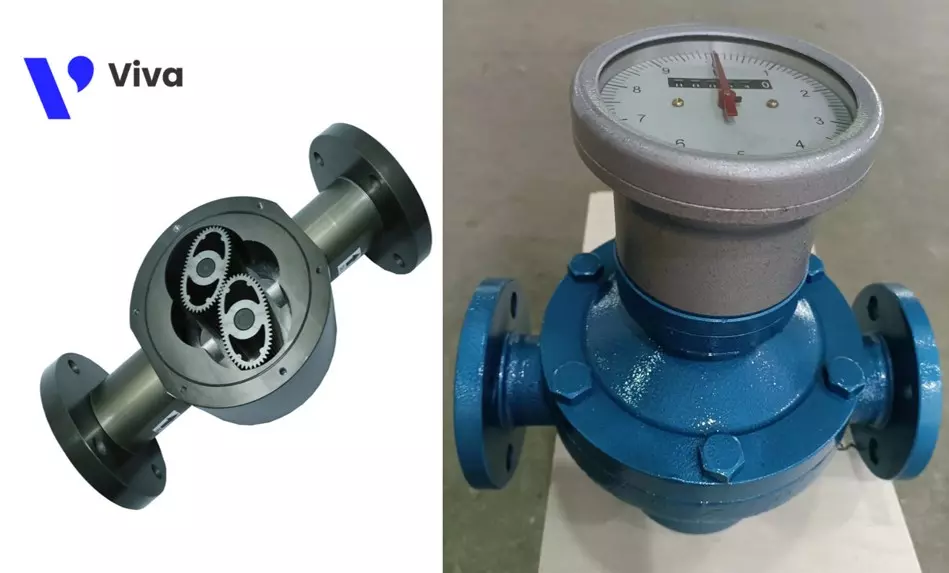
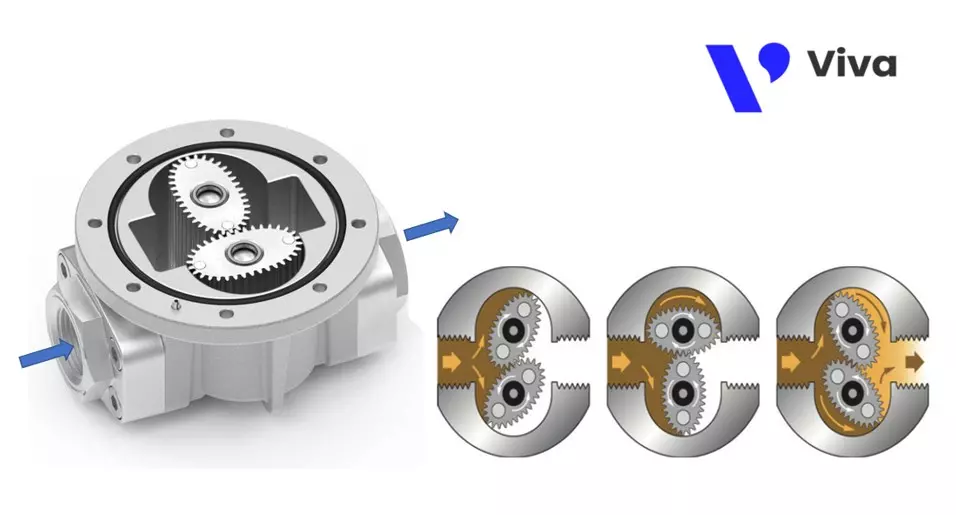
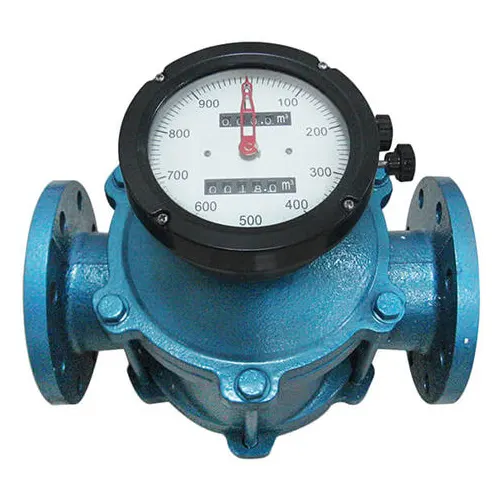
Oval gear oil flow meters
These devices utilize a pair of intermeshing oval-shaped gears. They are placed inside the valve body, and under the force exerted by the flowing fluid, these gears will rotate. This motion is transmitted through their shafts.
The rotational speed operates a counter in the case of mechanical meters or is encoded into an electrical signal in the case of electronic meters. The flow rate value is displayed on the meter face.
The special design of this device is particularly suitable for measuring the flow rate of petroleum products due to their relatively high viscosity.
Compared to turbine flow meters, this device is considered to have higher durability and better stability. The product line offers two options: mechanical and electronic versions.

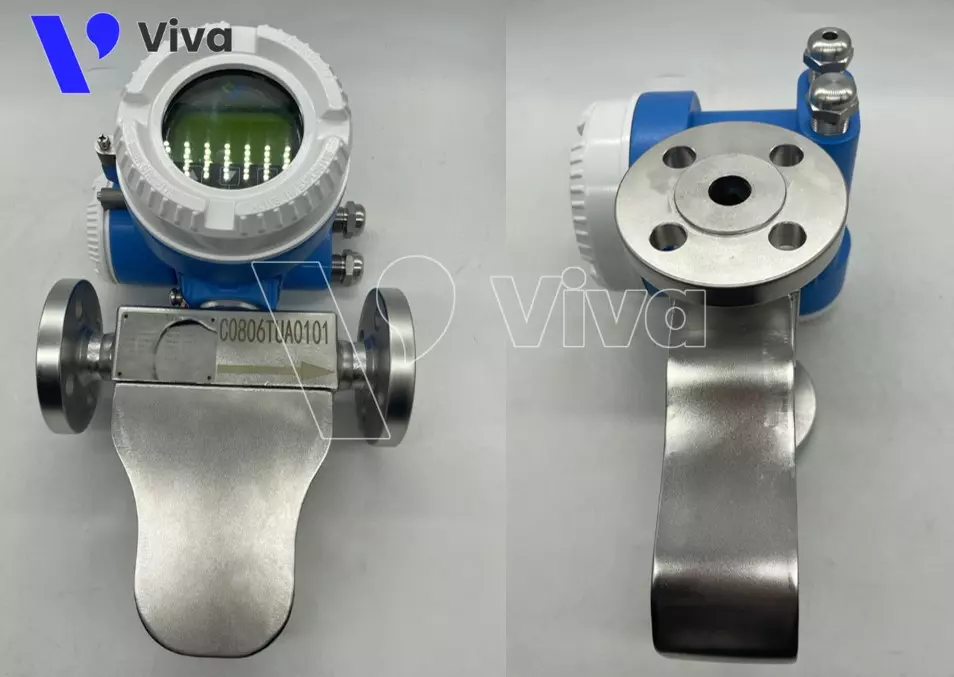
Coriolis-type oil flow meters
Coriolis-type oil flow meters are typically preferred for applications in systems that demand high accuracy. They are often used for calculating oil quantities in situations involving price calculations.
As you may know, crude oil or processed oil after refining goes through several stages, resulting in its relatively high cost. Therefore, during trade between parties, there is a need for a device capable of accurately measuring the flow rate of this fluid to ensure transparency. Coriolis flow meters fulfill this stringent requirement very well.
However, this line of flow meters has the highest price among other product lines. Consequently, they are less commonly used in general applications and are not extensively utilized in Vietnam compared to other flow meter types.

Structure and Operating Principles of Oil Flow Meters
In the previous section, I introduced several types of oil flow meters. To have a better understanding of them, let’s together explore the structure and operating principles of these meters.
Structure and Operating Principles of Turbine Oil Flow Meters
Turbine oil flow meters are constructed with the following basic components:
- Meter body: The meter body is made of stainless steel, aluminum alloy, or steel. Inside the meter body, there are turbine blades. The two ends of the meter body are designed for connection, with one end having a threaded connection for devices with small sizes, and the other end having a flange connection for devices with larger sizes.
- Display screen: An LCD screen is used to display the measured oil flow as it passes through the meter body, as well as other parameters during operation and device adjustment.
- Turbine blades: These components rotate when influenced by the flowing oil inside the meter body. They can be made of metal or special types of plastic. For devices with plastic turbine blades, magnets are often added inside them to interact with the sensor head.
- Speed sensor head: The sensor head is mounted directly above the turbine blades to collect information about the rotational speed and convert it into electrical signals for transmission to the electronic information processing network.
- Electronic circuitry: This component receives the signal information from the speed sensor head, combines it with pre-loaded computational equations and pre-adjusted parameters, and calculates the appropriate flow rate value. The electronic circuit operates using electrical energy, and the current used can be AC 220V, DC 24V, DC 12V, and so on (depending on the product type).

Structure and Operating Principles of Oval Gear Oil Flow Meters
Oval gear oil flow meters are composed of the following main components:
- Meter body: The meter body is usually made of carbon steel or stainless steel.
- Oval gear pair: The interlocking oval gear pair is installed inside the meter body. They will rotate when there is a flow of fluid passing through them. The rotational speed of this gear pair is proportional to the flow rate of the fluid.
- Gear shaft: The gear shaft is responsible for fixing and maintaining the rotational trajectory of the two gears placed within the meter body.
- Counter: The counter serves as a mechanical mechanism for analog meters or as a processing unit for electronic meters. This component converts the motion of the oval gear into a value representing the measured flow rate.
- Dial: The dial is the part that displays the measured flow rate value. The flow rate value is shown on the dial.
Applications of Oil Flow Meters
Oil flow meters can be used to measure the flow rate of gasoline, diesel, and other high-viscosity fluids. As you know, gasoline and diesel are crucial fuel sources used to operate various types of machinery, and they come at a considerable cost.
This creates a demand for devices capable of measuring the flow rate of these fluids.
Examples of the applications of oil flow meters include:
- Applications in large-scale machinery and vehicles: For large-sized vehicles such as ships, oversized trucks, and heavy-duty machinery, they consume a significant amount of oil during operation. It is important to control and monitor the oil consumption to calculate operating costs and estimate the appropriate fuel reserves for different situations.
- Industrial manufacturing: Oil is used to operate many types of industrial machinery and production lines. Fuel costs are a necessary expense and a part of the input cost that businesses need to understand in order to determine the selling price of their products.
- In trading transactions: As you are aware, crude oil, gasoline, and diesel are commonly traded commodities between countries and businesses. To determine the unit price for these products, it is essential to accurately measure the volume of oil exchanged between parties.
These are just some practical examples of the applications of oil flow meters, highlighting the importance of this product.

ĐÁNH GIÁ SẢN PHẨM












Đánh giá
Chưa có đánh giá nào.