Pneumatic cylinder
Giá gốc là: 300.000 ₫.285.000 ₫Giá hiện tại là: 285.000 ₫.
Cập nhật lần cuối ngày 20/07/2023 lúc 11:03 sáng
The compressed air system is widely used in various fields, in which the pneumatic cylinder (air cylinder) is one of the fundamental compressed air devices. They are classified as executing devices within each system.
In this article, we will explore together additional information about pneumatic cylinders, including their structure, operating principles, practical applications, and more.
Introduction to pneumatic cylinders
A pneumatic cylinder is a compressed air device used to generate rotational or linear motion through the pressure of compressed air acting on a piston. With a specially designed structure, it creates a pressure difference between the chambers inside the cylinder to achieve the desired motion.
To control the operation of this device, a key aspect is the control of the process of supplying and releasing compressed air to the chambers inside the cylinder.
This device is applied in numerous systems across various fields. Therefore, they are designed and manufactured in different types, corresponding to different functions and shapes. Most pneumatic cylinders are made of aluminum, while some are designed to operate under high impact conditions and are made of stainless steel.
They are widely applied in many industries, highly regarded for their transmission capabilities, stable and durable operation even under high intensity conditions.

Structure of pneumatic cylinders
As you may know, there are various types of pneumatic cylinders available today, each designed to optimize performance for specific systems and meet specific technical requirements.
Therefore, there are increasingly more designed and manufactured variants with certain differences in structure. In this part of the article, we will explore the structure of the basic pneumatic cylinder, which is also the most commonly used type.
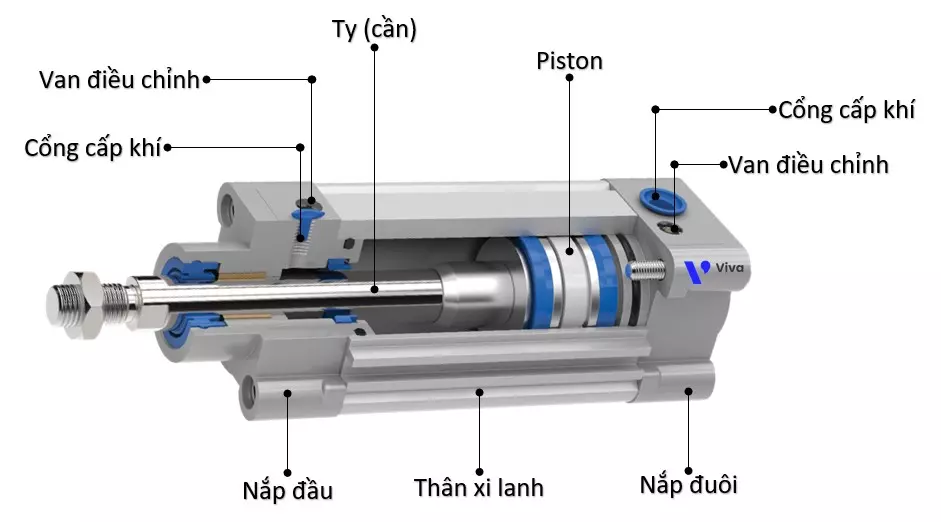
Pneumatic cylinders are composed of the following main components:
- Cylinder body: This component is typically made of aluminum or stainless steel and is designed in a cylindrical shape. The two common shapes are round and square cylinders. The inside of the cylinder body is hollow, with a diameter corresponding to the size of the piston.
- Cylinder caps: There are two corresponding parts, one at the head and one at the tail of the cylinder, depending on the pressure resistance requirements of the device. These two parts can be made of aluminum, steel, or stainless steel. Each cap is designed with air passages and includes a speed control valve for the cylinder’s stroke.
- Piston: This component receives the pressure of the compressed air and converts it into kinetic energy. It is placed inside the cylinder and connected to the piston rod. To ensure sealing and operational efficiency, the seal between the piston and the cylinder body is enhanced with rubber gaskets, and a thin oil film is maintained between them.
- Piston rod: It serves as the main driving component and also assists in guiding the motion of the piston. Therefore, piston rods are made of stainless steel, a material known for its corrosion resistance, high strength, and durability.
- Air ports: Air ports are designed at the ends of the cylinder. When air is supplied and the port below the piston rod is pressurized, the cylinder extends. When air is supplied to the upper port, the cylinder retracts.
- Control valves: Control valves are designed alongside the air ports and are responsible for controlling the extension and retraction speed of the pneumatic cylinder. Essentially, they are two flow control valves that regulate the flow of compressed air supplied inside the cylinder body through the inlet ports.
These are the main components that make up a pneumatic cylinder. In addition to these parts and components, there are also connecting elements and components that increase the cohesion between them, including gaskets, bolts, and bushings.
Operating principle of pneumatic cylinders
The operating principle of pneumatic cylinders is relatively simple and revolves around two main actions: extending the cylinder rod and retracting the cylinder rod. These actions are generated by the pressure difference acting on opposite sides of the piston, and this pressure difference is created by controlling the process of supplying compressed air into the cylinder.
Specifically, these two processes occur as follows:
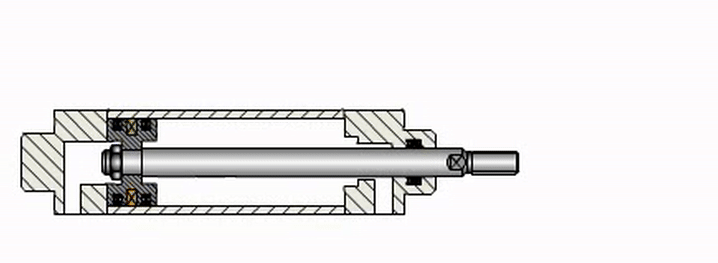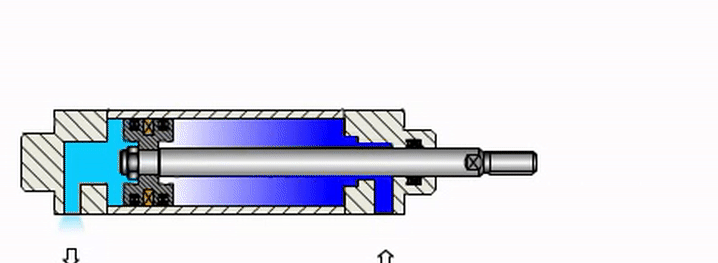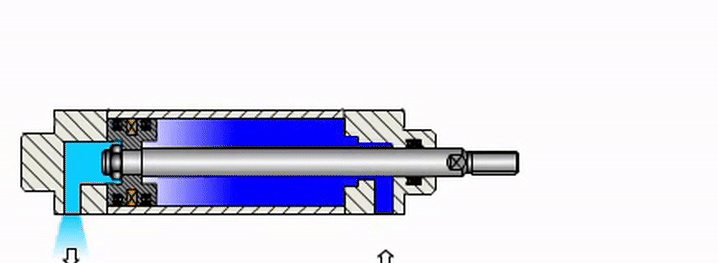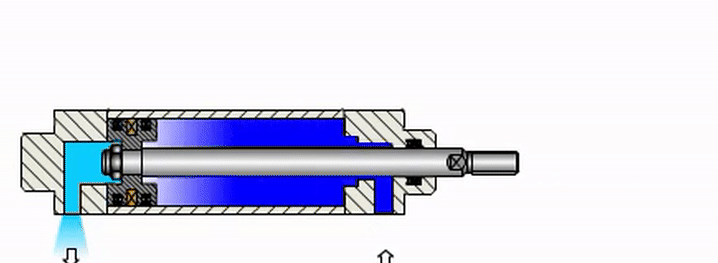
- Initially, the pneumatic cylinder is in the retracted position. When compressed air is supplied through the inlet port at the tail of the cylinder, the high pressure of the compressed air acts on the piston and the entire rear chamber. Due to the fixed design of other components, the piston will slide along the cylinder bore, along with the connected rod, resulting in simultaneous motion (the rod extends out of the cylinder body).
- The retraction of the cylinder rod is achieved by supplying air to the inlet port at the head of the cylinder. In this case, the pressure of the compressed air acts on the piston in the opposite direction. As a result, the piston moves backward, pulling the rod back into the cylinder.
Classification of pneumatic cylinders
Over time, with application and development, pneumatic cylinders have been used in almost every field, from simple to complex systems. Therefore, there have been numerous variations of this pneumatic device that have been researched and manufactured. Let’s now take a look at some types of pneumatic cylinders commonly used in practical applications.
Classification based on the type of pneumatic action
Single-acting Pneumatic Cylinder
A single-acting pneumatic cylinder is a device that operates by the unidirectional force from the compressed air while the opposite direction is affected by the spring force inside the cylinder body. Depending on the arrangement of the spring, they can be classified into two types:
- Air-to-push Cylinder: When we want the cylinder to perform a pushing action, we need to supply compressed air inside it, with sufficient pressure to generate a force acting on the piston greater than the force of the spring. When we stop supplying air, the spring force will act to return the cylinder to its initial position.
- Air-to-pull Cylinder: The cylinder remains in the extended position when not supplied with air. Only when we supply air into the cylinder body with sufficient pressure, the cylinder will retract.
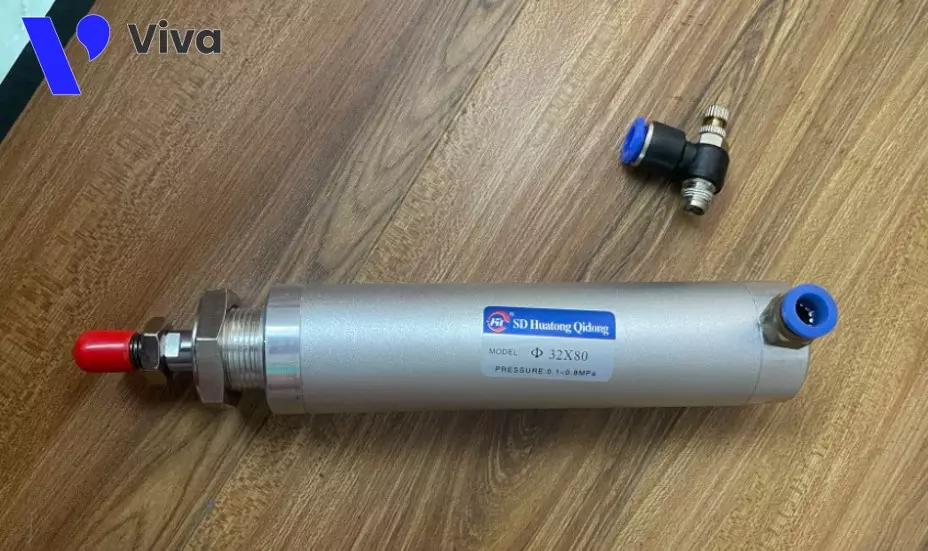

Double-acting pneumatic cylinder
Unlike the single-acting type that requires air supply from one end to change its operational state, the double-acting pneumatic cylinder requires air supply from both ends to control its retracting and extending actions. Since it doesn’t eliminate a portion of the force from the spring, the double-acting type usually uses higher-pressure compressed air (under the same size and working load conditions).
Furthermore, the double-acting type is highly regarded for its flexibility in applications. By changing the air supply ports, we can easily and quickly control the operation of this device.
For these reasons, the double-acting type is more commonly used compared to the single-acting type.
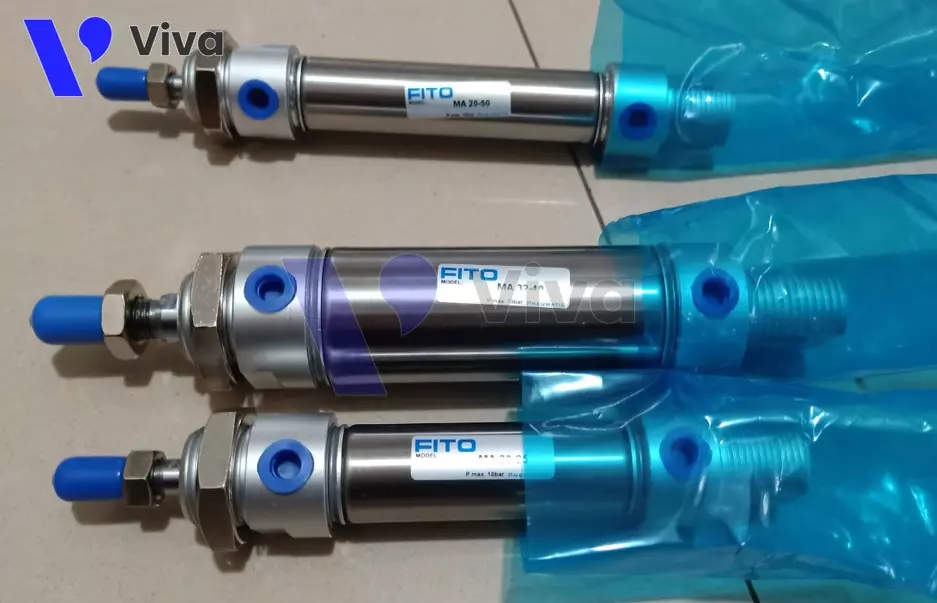

Classification based on shape
Square Pneumatic Cylinder
This device is designed with a square-shaped cylinder body or a cylindrical body with two cylinder end caps designed with a square cross-section.
In essence, both square and round cylinders have the same functionality and structural principles. However, square cylinders are typically designed with larger dimensions compared to the cylindrical form. They are often applied for installation in fixed positions.

Round Pneumatic Cylinder
As the name suggests, these devices are designed with a cylindrical outer shape. Compared to the square-shaped variant, round pneumatic cylinders are usually smaller in size, and the cylinder end cap integrates a mounting base component.
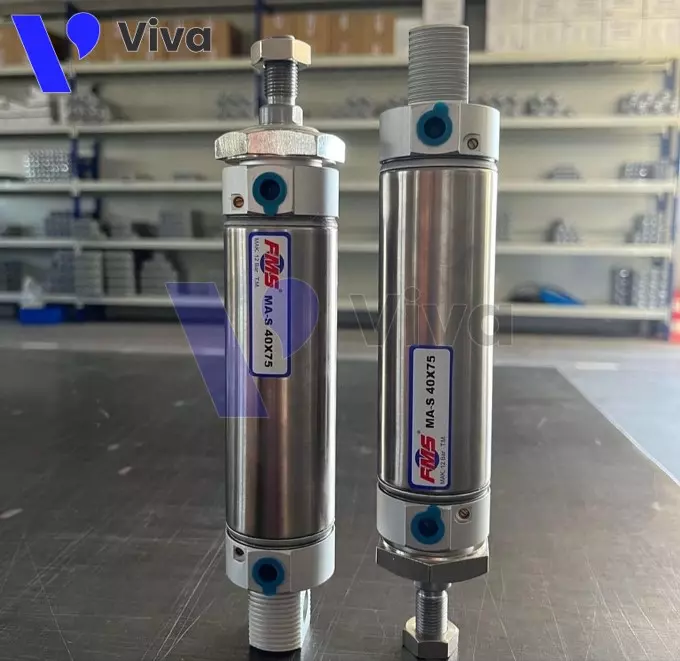

Compact pneumatic cylinder
Compact pneumatic cylinders are characterized by their compact design, often seen in the form of a square box or rectangular box shape.
They are designed to meet the requirements for a pneumatic cylinder device used in limited spaces while still achieving high performance in converting compressed air pressure into the actuating force of the cylinder shaft.
Compact pneumatic cylinders are typically made of aluminum or stainless steel, with diameters ranging from 8mm to 50mm and lengths from 10mm to 300mm. Due to their small size and high durability, they are commonly used in automation systems and small motor control.

Classification based on function
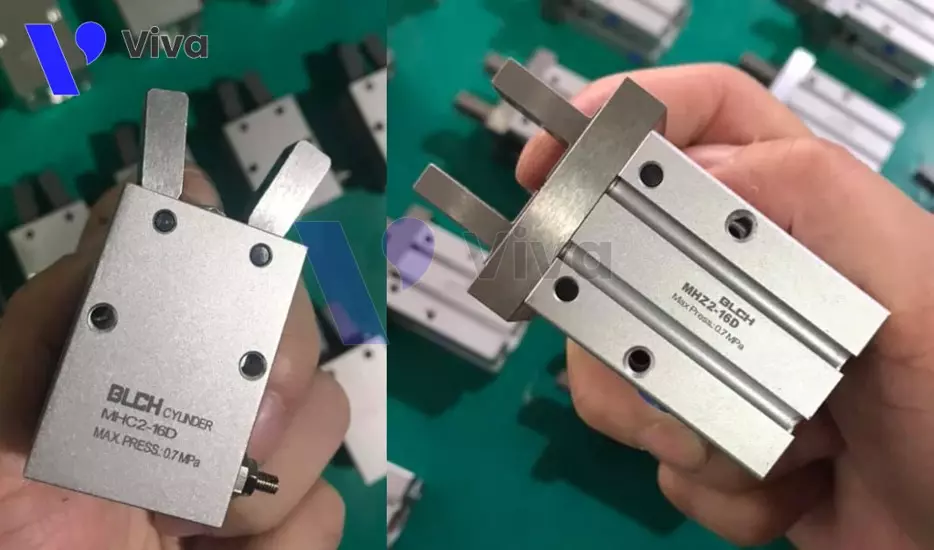
Clamp-type pneumatic cylinder
A clamp-type pneumatic cylinder is a type of cylinder that has a design that is more special than conventional pneumatic cylinder devices. It has two metal clamp heads designed parallel to each other, and they will clamp or open when there is a change in the pressure of the compressed air acting on the piston component inside the cylinder.
With such a structural characteristic, the device is used for fixed functions or clamping and then moving devices or objects during the production process, especially for automated systems.

Double-ended pneumatic cylinder
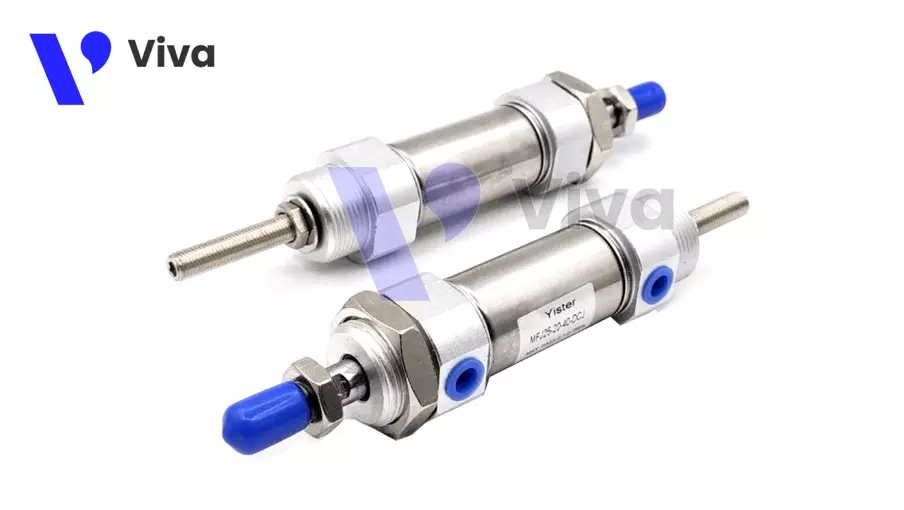
The double-ended pneumatic cylinder has a quite special design in which it has two coaxial cylinders symmetrically designed with each other, connected through a piston.
This type of cylinder is less commonly used in practical work, but if in large systems with complex structures, during the design phase, users intentionally arrange mechanisms to use this type of pneumatic cylinder, it will save initial costs for the system. Because if used properly, this device can simultaneously perform the functions of two conventional devices.

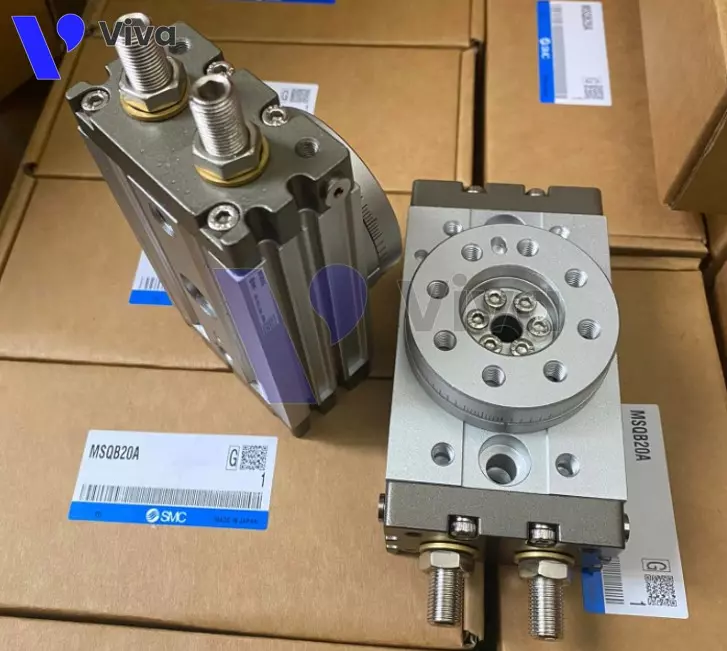
Rotary pneumatic cylinder
A rotary pneumatic cylinder utilizes high-pressure compressed air to generate rotary motion. The angle of rotation depends on the manufacturer’s design, but two common angle limits are 90° and 180°.
The rotary pneumatic cylinder is designed with two options for the actuation of compressed air, including:
- Single-acting rotary pneumatic cylinder: Inside the cylinder body, a spring system is placed to constantly apply a spring force to the piston, thereby maintaining a force to position the cylinder at a predetermined rotation angle. To change the tilt angle of the cylinder, compressed air at a sufficient pressure is supplied to the body, at which point the force exerted by the compressed air overcomes the force from the spring, causing the cylinder to change its rotation angle. When the air supply is stopped, the spring force automatically returns the cylinder to its initial position.
- Double-acting rotary pneumatic cylinder: This device is designed with two air supply ports on its body, corresponding to two opposite rotational directions.
With its unique design and operation characteristics, rotary pneumatic cylinders are often used as driving components, as rotary tables, to serve in certain stages of the production process.

Some brands of pneumatic cylinders
At the current time, we are fully capable of producing pneumatic cylinders. However, due to some technical limitations, if we were to produce these products ourselves, we would not have enough capability to compete in terms of cost-effectiveness and technical aspects with imported products.
That’s why most of the pneumatic cylinders being used in Vietnam are imported products from various brands.
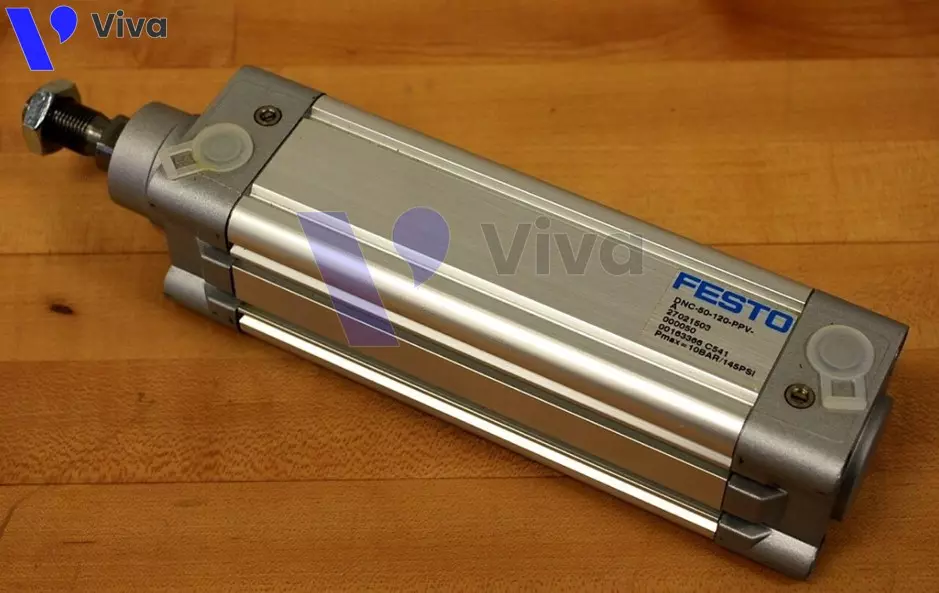
Festo Pneumatic Cylinders (Germany)
FESTO is a famous brand from Germany specializing in the manufacture of pneumatic devices, copper transmission devices, control devices, and more. German-branded products have long been highly regarded for their durability and stability. In order for these products to be put into use, they must meet stringent requirements set by the European market, one of the most demanding markets.
Although Festo pneumatic cylinders are more expensive compared to many other brands, they are prioritized for use in various machinery systems due to the superior quality they provide.

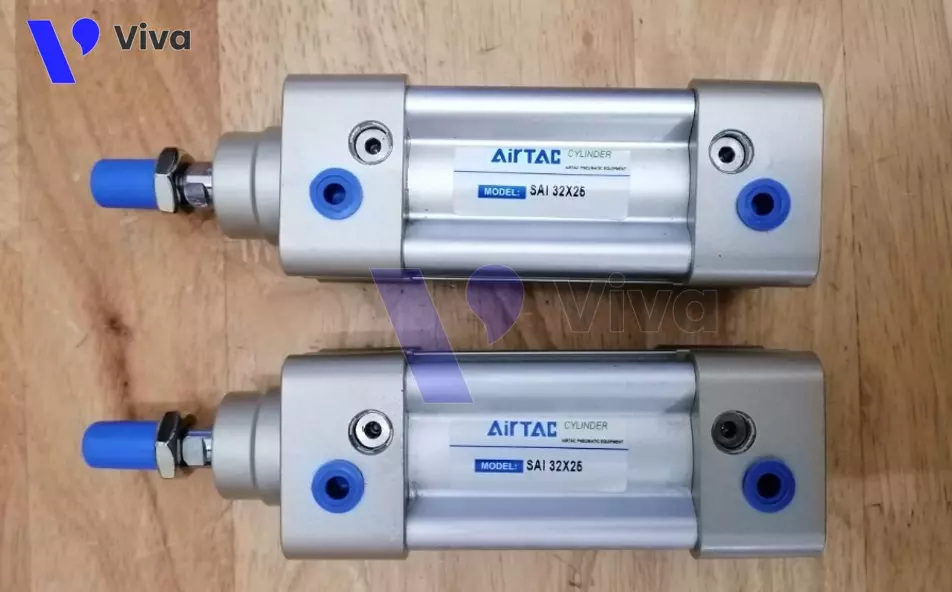
Airtac Pneumatic Cylinders (Taiwan)
The Airtac brand from Taiwan is surely familiar to customers with experience working with pneumatic systems. The company provides a wide range of different pneumatic devices for use in automated machinery systems. Airtac products, in general, and Airtac pneumatic cylinders, in particular, are used in various small and large systems in Vietnam due to their low cost.

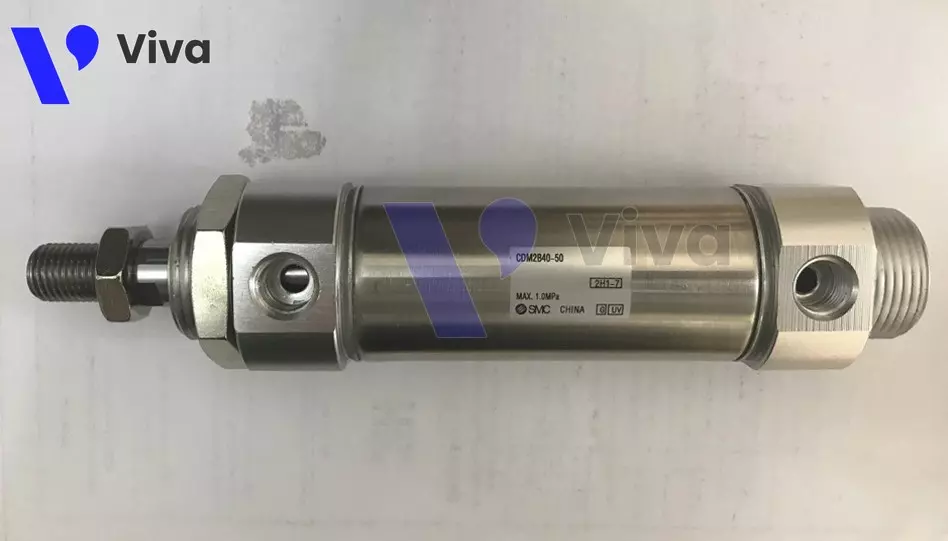
SMC Pneumatic Cylinders (Japan)
SMC is a famous brand from Japan specializing in the production of products for pneumatic systems, such as pneumatic valves, air filters, pneumatic cylinders, shock absorbers, and various other types of products. SMC products are widely used in industries such as manufacturing, mechanical engineering, automation, electronics, and machinery manufacturing. Manufactured using Japanese technology, SMC pneumatic cylinders fully comply with European standards, allowing their products to be present in numerous markets worldwide.

Types of accessories used for pneumatic cylinders
To ensure the efficient operation of pneumatic cylinders and meet various working conditions, pneumatic cylinder devices need to be installed in the working system, along with the installation of compressed air supply lines into the cylinder. And to carry out these tasks, the use of accompanying accessories is essential.
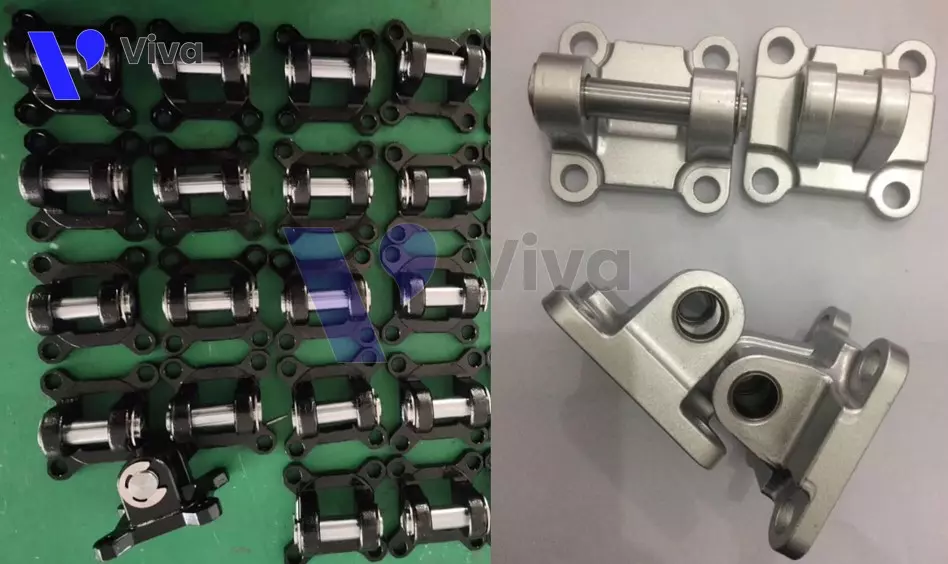
Cylinder bases
Cylinder bases are important components for many systems that use cylinders. They are used to mount the cylinders onto surfaces or connect the cylinders with other parts in the system.
In terms of materials, these accessories can be made from various materials such as aluminum, steel, or plastic. They can be designed in different sizes and shapes to fit the requirements of the application. Some cylinder bases have additional features, such as center of gravity adjustment or customization for height and tilt adjustment of the cylinder. They can be directly mounted on the cylinder or through intermediate components such as threaded adapters or connectors.

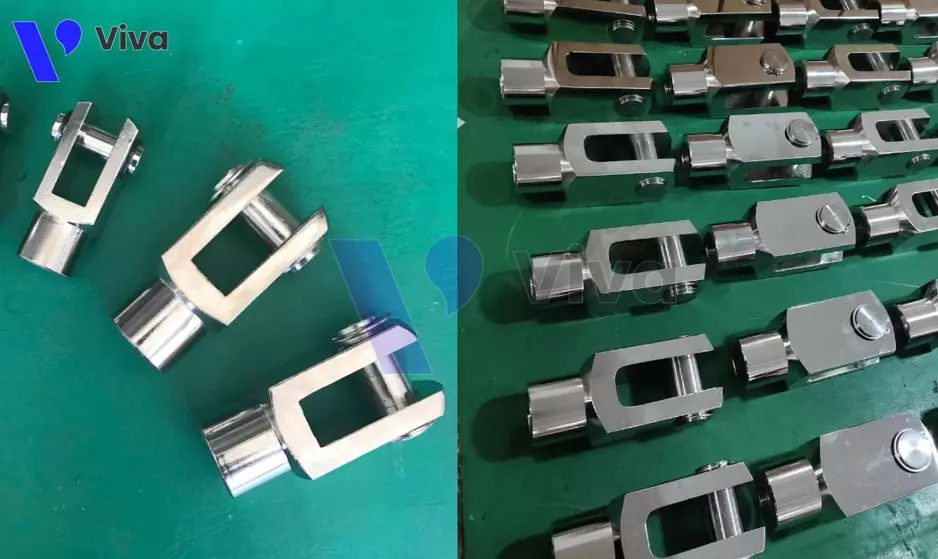
Cylinder shaft connector
If the cylinder base is used to mount the rear part of general cylinder devices, including pneumatic cylinders, the cylinder shaft connector is connected to the rod end of the cylinder (also known as the piston rod) to link with subsequent devices or mechanisms.
The connector part with the cylinder shaft is specially fabricated and connected to the piston rod through threaded connections, snap connections, or using metal pins.
As a component responsible for transmitting motion and force, this accessory is made from alloys or metals, and the most common material used is stainless steel 304.

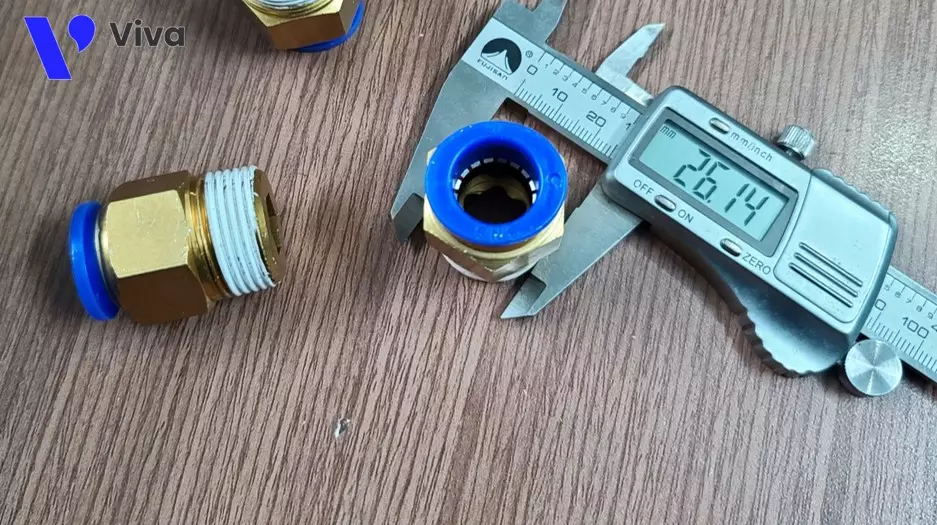
Pneumatic quick connector
The pneumatic quick connector is used to connect the cylinder with the air hose (compressed air supply line). The advantages of using pneumatic quick connectors are easy and fast connection, stable joints, ensuring tightness, and allowing easy disassembly of components and devices from the system in many cases.
Quick connectors are usually made from brass or stainless steel.

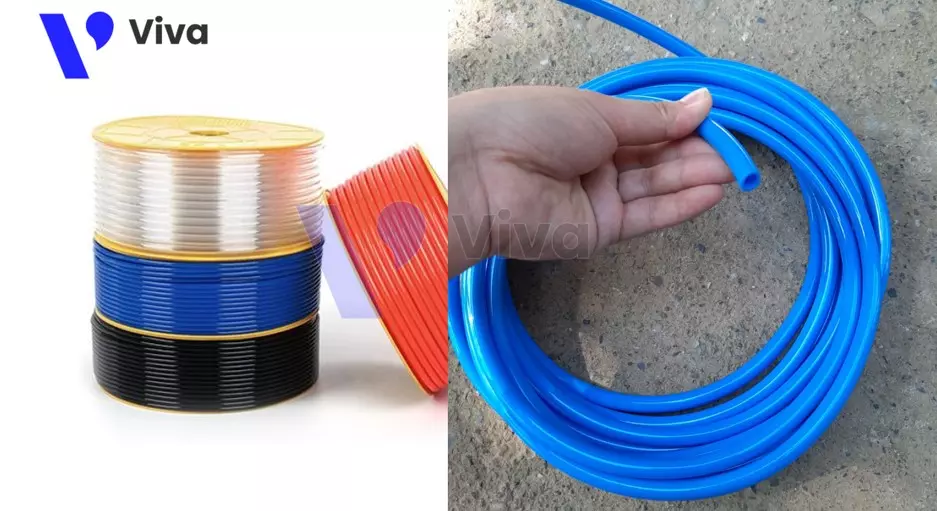
Pneumatic air hose
The pneumatic air hose is used to convey compressed air from the pressure vessel to all pneumatic devices within the system. Therefore, they play a crucial role, and there are different types of air hoses made from materials such as PVC, PU, synthetic rubber, etc.

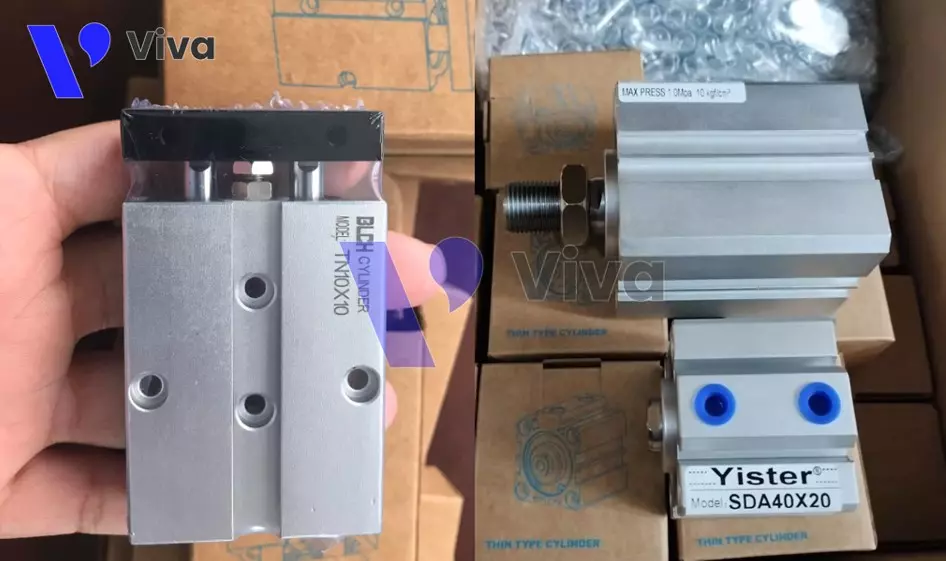
Symbols for dimensions of pneumatic cylinders
The symbols for dimensions of pneumatic cylinders are simple and easy to understand if you have worked with this type of device before. You probably already grasp the meaning behind the symbols for cylinder dimensions. However, during customer support, I have encountered some customers asking questions about the markings on the cylinder body. Therefore, I would like to share this information in the hope that after reading, readers will have a better understanding of the symbols for equipment dimensions.
Depending on the manufacturer, different model designation methods may be used.
For example, in the image below, we have “GDC 40×20”. Here, “GDC” is a specific model designation for each product line (various manufacturers may have different designation methods). “20” represents the inner diameter of the cylinder, which is 20mm, and “40” represents the stroke length of the piston rod, which is 40mm (in many cases, the designation may be reversed, so it is important to combine the dimensions with visual observation).
In reality, pneumatic cylinders are provided with limited size options. The stroke length of the piston rod can range from 10mm, 25mm, 50mm, to 1000mm. The inner diameter of the cylinder can range from 12mm, 16mm, 20mm, to 320mm.

Calculating the Impact Force and Speed of Pneumatic Cylinders
During the calculation and initial design phase, in order to select pneumatic cylinder devices that are suitable for the specified technical requirements, apart from determining parameters such as size, features, temperature, and working pressure,…
It is also essential to calculate and determine the thrust force and pulling force of the cylinder. Skipping this calculation step can result in choosing a cylinder with excessive or insufficient force, which can lead to system malfunction or damage to related equipment.
- To choose a cylinder with appropriate impact force and control the force of the pneumatic cylinder during operation, we can rely on the following formula:
F = P x A
Where:
F – Impact force of the piston rod (N)
P – Pressure of the supplied compressed air to the cylinder (Pa)
A – Piston face area (m²).
Using the above formula within the allowed limits, users can adjust the compressed air pressure to control the impact force of the piston rod (F).
- The speed of the pneumatic cylinder, which refers to the extension and retraction speed of the piston rod during operation, under ideal working conditions, can be calculated using the following formula:
V = Q/A
Where:
V – Speed of the piston rod (m/s)
Q – Flow rate of the compressed air entering the cylinder (m³/s)
A – Contact area of the piston face with the compressed air (m²).
Each pneumatic cylinder is equipped with two integrated flow control valves that can adjust the flow rate of the compressed air entering the cylinder (Q). Therefore, within the allowed limits, the working speed of the cylinder can be regulated using these two flow control valves.
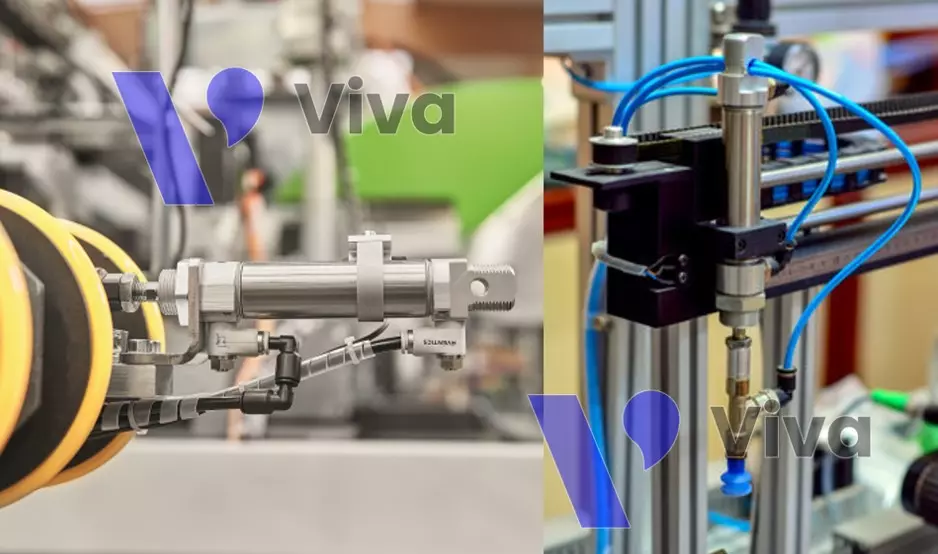
Applications of Pneumatic Cylinders
Pneumatic cylinders are essential components in pneumatic systems and are widely used in various applications. With their diverse and extensive range, these devices find applications in fields such as mechanical engineering, mining, transportation, and more.
Here are some examples of the applications of pneumatic cylinders:
- Transportation applications include: ships, cars, airplanes, and more.
- Industrial machinery applications: CNC milling machines, CNC lathes, various types of pneumatic punching machines, and more.
- Automation line applications: Manufacturing assembly lines for machine components, food production lines, assembly lines, and more.

Conclusion
Pneumatic cylinders are important devices used in various fields, providing efficient solutions for tasks, labor-saving, and improving work performance.
Within the scope of this article, we have attempted to convey basic information about pneumatic cylinders, hoping that it will provide useful information to our readers and customers.
We warmly welcome feedback from our readers. If you have any further questions regarding these devices, including features, technical specifications, or support for purchasing and sales, please feel free to contact us directly for more detailed discussions.
Thank you!

ĐÁNH GIÁ SẢN PHẨM












Đánh giá
Chưa có đánh giá nào.