What is pneumatic?
Pneumatic is one of the important elements in many modern industries, especially in manufacturing, fabrication, and assembly of equipment and machinery. To use and control pneumatic effectively, one needs to have a clear understanding of the concept of “pneumatic” and its components and properties. This article will provide you with information about pneumatic, from its definition to its operation, applications in daily life and industry. With rich and detailed content, this article hopes to help you gain a better understanding of pneumatic and apply it effectively in practice.
What is Pneumatic? – Development History
What is the concept of pneumatic?
What is pneumatic? Pneumatic is a type of gas that is compressed and stored in high-pressure containers. Pneumatic is commonly used in industrial and construction applications such as surface cleaning, spray painting, powering tools and machinery, etc.

To generate pneumatic, air compressors are used to compress air or other gas mixtures to the desired pressure. The pneumatic is then stored in high-pressure containers for later use.
In pneumatic systems, the main components include air compressors, air storage tanks, control valves, air ducts, and other connecting parts. These systems are often controlled by automatic controllers to help regulate pressure and airflow.
Main Components
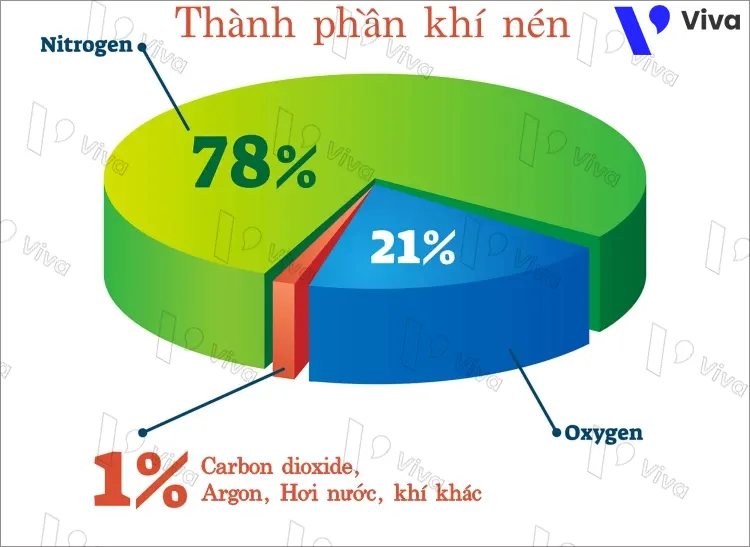
Pneumatic is a mixture of gases, typically composed of colorless, odorless, and tasteless gases such as Nitrogen (N2) 78% and Oxygen (O2) 21%. However, the main components of pneumatic can vary depending on the purpose of use and the method of generation.
In addition to Nitrogen and Oxygen, pneumatic can also contain other gases such as Argon (Ar), Hydrogen (H2), Carbon Dioxide (CO2), and Hydrofluorocarbon (HFC). The composition of pneumatic can be adjusted by regulating the amount of different gases mixed together.
Development History
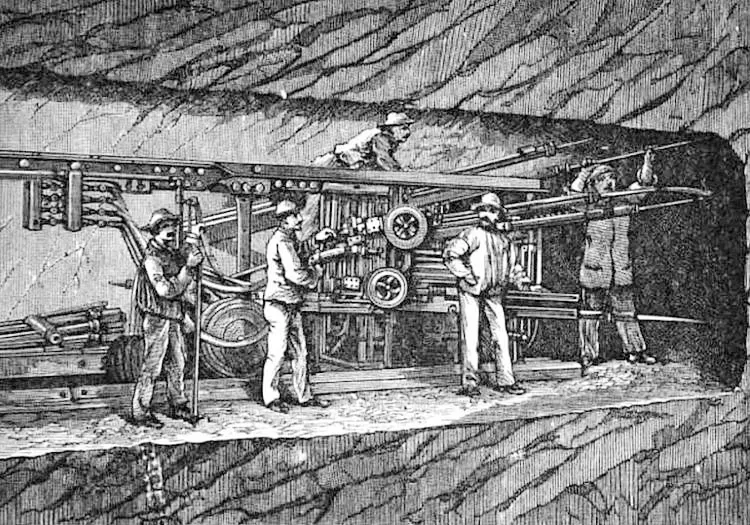
Pneumatic has been used in industries for a long time; however, its development and application were greatly accelerated in the 19th century.
In the 19th century, pneumatic was widely used in the shipbuilding and mechanical engineering industries. The initial applications of pneumatic included pushing, cutting, drilling, grinding, and sandblasting. The use of pneumatic helped improve productivity and efficiency in the manufacturing process.
By the late 19th century, pneumatic was extensively employed in the electronics manufacturing industry, such as in the production of electric bulbs. The use of pneumatic enhanced the production process and ensured product quality.
In the 20th century, pneumatic continued to be widely used in various industries and applied to diverse applications, from automobile manufacturing to food production. Nowadays, pneumatic is extensively utilized in industrial production processes to ensure efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness.
Characteristics of Pneumatic
– Pressure: Pneumatic is stored at a higher pressure than atmospheric air. The pressure of pneumatic typically ranges from a few psi to thousands of psi, depending on the specific application. Evaluating and controlling the pressure of pneumatic during its usage is crucial for safety and efficiency.
– Volume: Pneumatic has a lower volume compared to atmospheric air. This means that the mass of gas contained in a given space of pneumatic is less than that of atmospheric air. Therefore, when using pneumatic, it is necessary to calculate the volume of air to ensure safety and efficiency.
– High Density: When compressed, the density of air increases. This implies that the mass of gas contained in a given space increases. Therefore, when using pneumatic, it is essential to calculate the density of air to ensure safety and efficiency.
– Easy Storage and Transport: Pneumatic can be stored and transported in gas cylinders or through air pipelines. This helps minimize storage and transportation space compared to other forms of energy such as oil or gas.
– Stability: Pneumatic exhibits high stability, meaning that its pressure changes minimally during usage. This ensures the effective and reliable use of pneumatic during operations.
– Cleanliness: Pneumatic has high cleanliness and contains fewer harmful substances, making it suitable for applications that require cleanliness, such as in the food industry, pharmaceuticals, and electronic product manufacturing.
– Ease of Use: Pneumatic can be used to supply energy to tools and machinery through easily accessible air connectors. It can also be utilized for surface cleaning, spray painting, and other applications.
Generating Pneumatic
In daily life
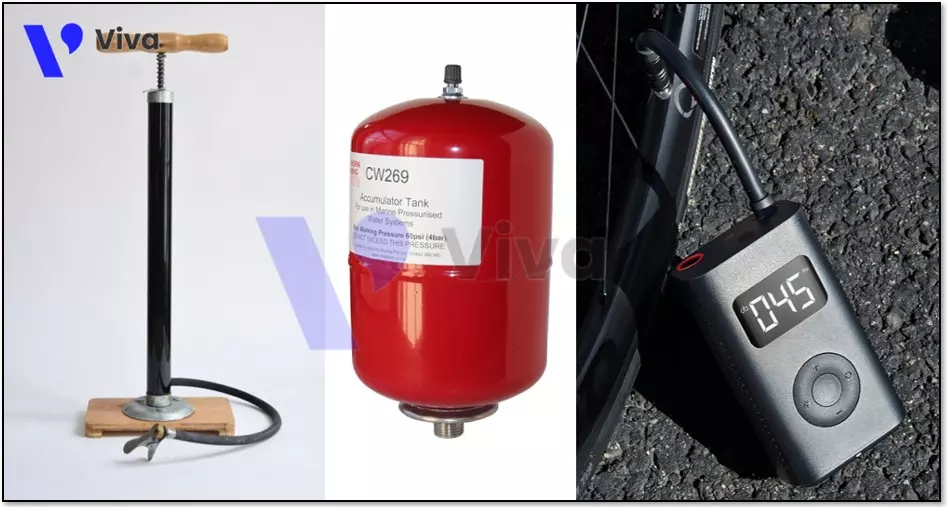
Pneumatic is widely used in everyday life and can be generated through the following simple methods:
- Using a hand pump or electric pump to inflate bicycle or car tires. The pump compresses air into the tire at a higher pressure than normal.
- Using a pneumatic tank to generate pneumatic. A pneumatic tank is a container that can store air at high pressure and can be used for spray painting, dusting, or inflating electronic devices.
- Using an air pump or foam generator to create air bubbles. An air pump uses a compressor to generate pneumatic and pushes it through a tube to create bubbles. A foam generator also uses pneumatic to create foam.
- Using a CO2 canister to generate pneumatic. CO2 canisters are used in sports activities such as shooting or beer brewing to generate CO2 gas. CO2 gas is compressed into the canister and can be used to generate high pressure for shooting or to create carbonation in the beer brewing process.

In industry
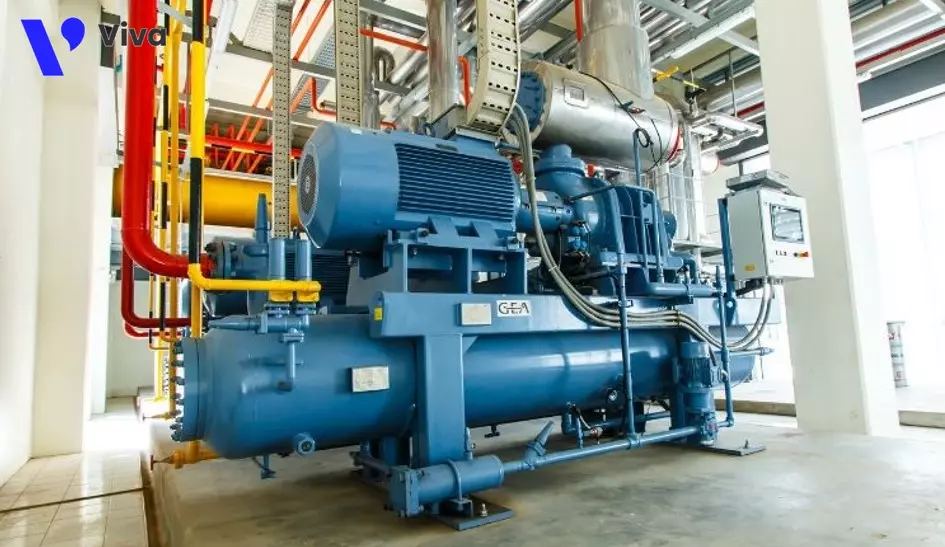
Methods of generating pneumatic in the industry can be complex and require specialized expertise. The most common method of generating pneumatic is by using an air compressor, a specialized device that compresses air into a storage tank capable of holding and storing air at high pressure. Air compressors can be divided into two main types:
- Centrifugal air compressors: This type of machine uses rotating components to compress air. Air is drawn into the rotating shaft and compressed within the empty space on the shaft. The pneumatic is then discharged and transferred to the storage tank.
- Reciprocating air compressors: This type of machine uses a piston to compress air. Air is drawn into the piston chamber and compressed as the piston moves upward. The pneumatic is then discharged and transferred to the storage tank.
There are also chemical methods such as: Utilizing chemical decomposition: Some chemicals such as ammonia and nitrate can undergo decomposition to generate pneumatic. This process is known as decomposition reaction and will release pneumatic as a byproduct.

Applications of Pneumatic
In Daily Life
Pneumatic is an important source of energy and has many applications in daily life. Here are some applications of pneumatic in everyday life:
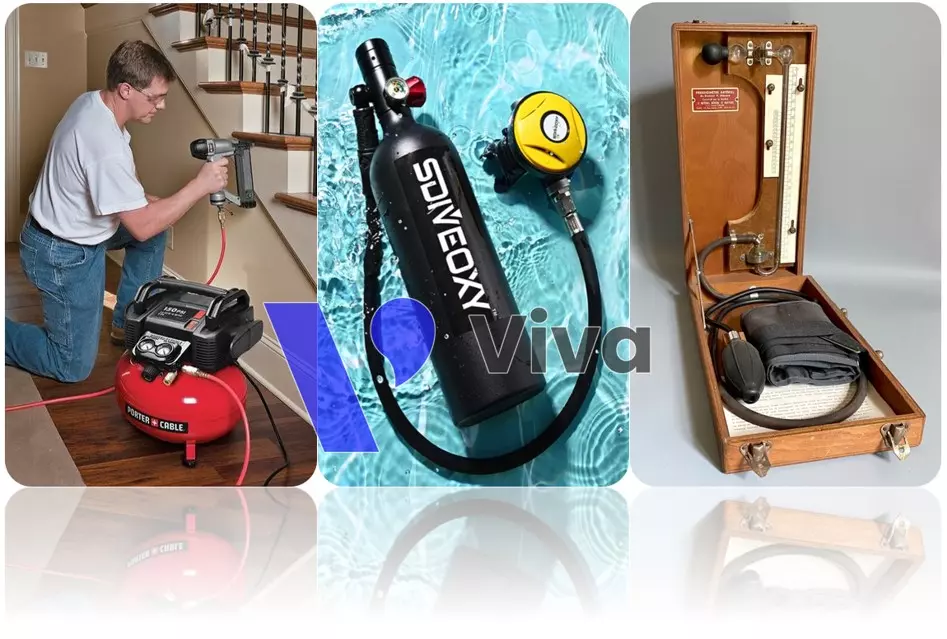
- Using pneumatic for pumping bicycles and cars: In some cases, using a hand pump to inflate bicycles or cars can be time-consuming and labor-intensive. Using pneumatic for tire inflation provides a convenient and quick solution.
- Using pneumatic in tools: Pneumatic is widely used in mechanical tools such as drills, grinders, nail guns, saws, etc. Pneumatic helps increase pressure and provide enough energy to work with hard materials.
- Using pneumatic in car wash machines: Pneumatic is used to generate high pressure in car wash machines, facilitating the cleaning of dirt and residues on the vehicle’s surface.
- Using pneumatic in medical diagnosis and treatment: Pneumatic is used in medical diagnosis and treatment, such as in respiratory devices like ventilators, oxygen concentrators, etc.
- Using pneumatic in the food and beverage industry: Pneumatic is used for packaging food and beverages in vacuum-sealed containers. Additionally, pneumatic is also used in the production of beer and wine to create high-pressure products.
Pneumatic has many other applications as well.

In Industry
Pneumatic is widely used in the industry due to its versatility, reliability, and high efficiency. Here are some examples of the applications of pneumatic in the industry:
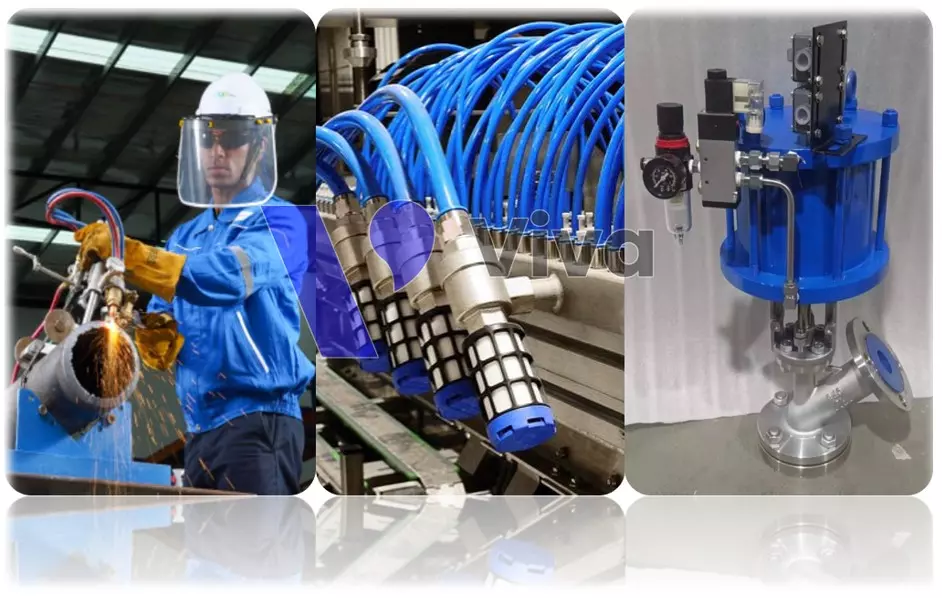
- Control and regulation: Pneumatic is used to control and regulate devices such as valves, filters, pumps, etc. In the production process, pneumatic can be used to control and position devices to ensure accurate and efficient operations.
- Manufacturing: Pneumatic is used to power machinery and equipment in manufacturing, such as compressors, cutters, grinders, etc. Pneumatic can also be used to supply oxygen for welding or metal cutting processes.
- Operation and maintenance: Pneumatic is used to operate and maintain production equipment such as air compressors, air dryers, air storage tanks, etc. It can also be used for blowing off parts or removing dust and dirt from equipment.
- Testing and measurement: Pneumatic is also used to test and measure the pressure and flow of various devices and systems, such as air compressors, air storage tanks, etc.
- Operation of other machinery and equipment: Pneumatic is also used to operate various machinery and equipment, such as elevators, automatic doors, fire suppression systems
Pneumatic plays a vital role in many industries, from automobile manufacturing to electronics, steel, plastics, and food production…

Some Types of Industrial Valves Operated by Pneumatic
Valves are important devices in industrial systems used to control the flow of liquids or gases within a system. Among them, there are some types of industrial valves operated by pneumatic, commonly used in various industries. Here are some types of industrial valves operated by pneumatic:
Pneumatically Controlled Butterfly Valve: A butterfly valve is used to control the flow of liquid or gas by rotating a disc within a pipe. The butterfly valve is actuated by pneumatic through a control system, which helps control the flow rate of the substance in the system.
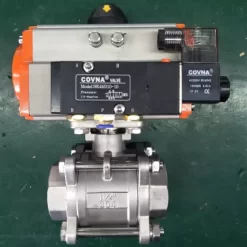
Pneumatically Controlled Ball Valve: This type of valve is used to control the flow of liquid or gas by rotating a ball. The pneumatically controlled ball valve is activated through a control system, which helps control the flow rate of the substance in the system.
Pneumatically Controlled Gate Valve: This valve is used to control the flow of pneumatic in a system. The valve is activated by pneumatic and can be configured to operate at different pressures.
Pneumatically Controlled Float Valve: This valve is used to control the water level in a tank or container. The valve is activated by pneumatic and can be configured to adjust the water level in the tank or container.
Pneumatically operated industrial valves help control the flow of liquid or gas in industrial systems. They are widely used in various industries and play an important role in reducing production costs and increasing production efficiency.
Summary of the Pneumatic Article
This article has explained the concept of pneumatic, including the characteristics and properties of pneumatic, how pneumatic is generated in daily life and industry, the applications of pneumatic in daily life and industry, the origin and history of pneumatic, and the main components of pneumatic.
It has also introduced some types of industrial valves that operate with pneumatic.
The overall overview of this article is to help readers understand pneumatic and its role in daily life and industry.